Introduction
Air compressors for plastic industry are indispensable tools powering critical manufacturing processes like injection molding, blow molding, and extrusion. These systems ensure precision, energy efficiency, and consistent output in a sector projected to grow by 4.2% annually through 2030. From reducing operational costs to supporting sustainable production, air compressors play a pivotal role in modern plastic manufacturing. This guide explores how choosing the right compressor technology can elevate your facility’s performance while aligning with industry demands for speed, reliability, and eco-efficiency.
Table of Contents
- Why Air Compressors Are Vital in the Plastic Industry
- Types of Air Compressors Used in Plastic Manufacturing
- 2.1 Rotary Screw Compressors
- 2.2 Piston Compressors
- 2.3 Centrifugal Compressors
- 2.4 Scroll Compressors
- Key Applications of Compressed Air in Plastic Production
- How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Facility
- 4.1 Assessing Air Demand
- 4.2 Energy Efficiency Considerations
- 4.3 Noise and Space Constraints
- Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity and Efficiency
- Case Study: Reducing Downtime in a Plastic Injection Molding Plant
- FAQs About Air Compressors in the Plastic Industry
1. Why Air Compressors Are Vital in the Plastic Industry
Compressed air is the invisible workhorse of plastic manufacturing. From powering pneumatic tools to enabling precise control in molding machines, it ensures:
- Consistent Product Quality: Air compressors regulate pressure during injection molding, minimizing defects.
- Automation Support: Robotics and conveyor systems rely on compressed air for seamless operation.
- Cost Efficiency: Modern compressors reduce energy consumption by up to 30%, lowering operational costs.
- Sustainability: Oil-free compressors prevent contamination, aligning with eco-friendly production goals.
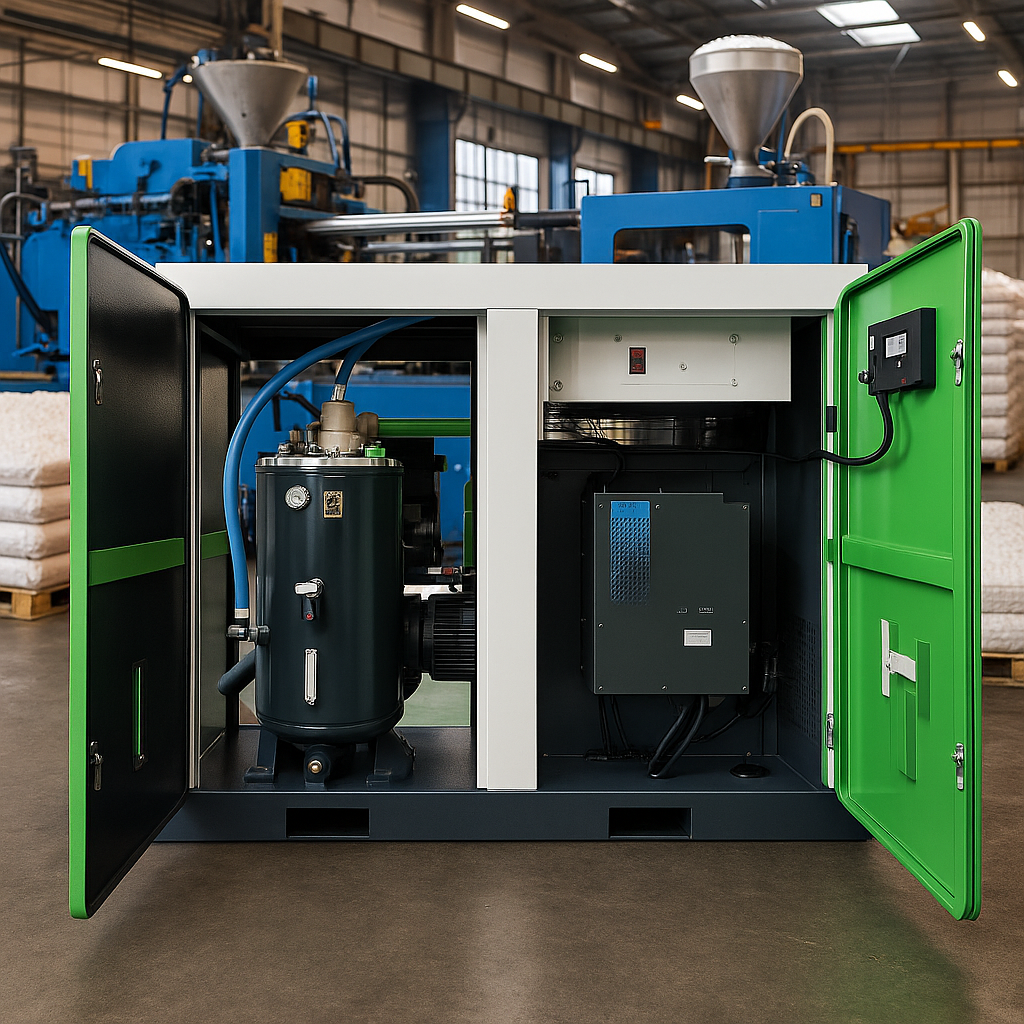

2. Types of Air Compressors Used in Plastic Manufacturing
2.1 Rotary Screw Compressors
How They Work: Twin screws rotate to compress air continuously, delivering steady airflow.
Best For: High-demand applications like blow molding and extrusion.
Advantages:
- 24/7 operation capability.
- Energy-efficient at partial loads (via variable speed drives).
- Low maintenance due to fewer moving parts.
2.2 Piston Compressors
How They Work: Reciprocating pistons compress air in a cyclic motion.
Best For: Small-scale operations or intermittent use.
Drawbacks: Higher noise levels and vibration; not ideal for continuous workflows.
2.3 Centrifugal Compressors
How They Work: High-speed impellers generate airflow kinetically.
Best For: Large facilities needing 2,000+ CFM output.
Advantages:
- Oil-free operation.
- Minimal maintenance.
2.4 Scroll Compressors
How They Work: Two spiral-shaped scrolls compress air with zero metal-to-metal contact.
Best For: Clean environments requiring oil-free air (e.g., medical plastics).
3. Key Applications of Compressed Air in Plastic Production
- Injection Molding: Compressed air ejects finished parts and controls clamping mechanisms.
- Blow Molding: Creates hollow products (e.g., bottles) by inflating heated plastic parisons.
- Pellet Conveying: Transfers raw plastic pellets using pneumatic systems.
- Cooling Systems: Accelerates cooling of molds to shorten cycle times.
4. How to Choose the Right Air Compressor for Your Facility
4.1 Assessing Air Demand
Calculate your facility’s CFM (cubic feet per minute) requirements using tools like the Compressed Air Challenge’s Air Demand Analysis Toolkit. Factor in:
- Peak vs. average demand.
- Future expansion plans.
4.2 Energy Efficiency Considerations
- Opt for Variable Speed Drive (VSD) compressors to match output with real-time demand.
- Look for ISO 50001 certification or ENERGY STAR® ratings.
4.3 Noise and Space Constraints
- Rotary screw compressors operate at 70–75 dB, ideal for indoor use.
- Compact designs (e.g., vertical scroll compressors) save floor space.
5. Maintenance Best Practices for Longevity and Efficiency
- Daily: Check for leaks using ultrasonic detectors.
- Monthly: Replace air filters and inspect belts.
- Annually: Test safety valves and upgrade control software.
Pro Tip: Partner with a certified technician for predictive maintenance using IoT sensors.
6. Case Study: Reducing Downtime in a Plastic Injection Molding Plant
A mid-sized manufacturer in Ohio reduced downtime by 40% after upgrading to a VSD rotary screw compressor. By aligning airflow with machine cycles, they achieved:
- 25% lower energy bills.
- 15% faster production rates.
7. FAQs About Air Compressors in the Plastic Industry
Q: Which compressor type is best for high-volume extrusion?
A: Centrifugal or rotary screw compressors, depending on CFM needs.
Q: How often should I replace compressor oil?
A: Every 8,000 hours for rotary screw models; follow OEM guidelines.
Q: Can I use a single compressor for multiple machines?
A: Yes, but ensure your system includes a reliable dryer and distribution network.
Conclusion
Investing in the right air compressor system transforms plastic manufacturing efficiency, reduces costs, and supports sustainability. By partnering with experts and prioritizing maintenance, facilities can unlock long-term ROI while meeting growing industry demands.
Ready to Optimize Your Compressed Air System?
[Contact us today] for a free audit and discover tailored solutions for your plastic production needs.
 Английский
Английский
 Русский
Русский
 Французский
Французский
 Испанский
Испанский
 Арабский
Арабский